APAC ex-JP
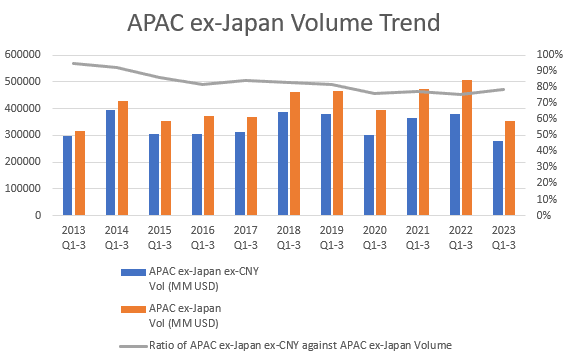
The APAC ex-Japan syndicated loans market volume in the first 3 quarters of 2023 dropped by 30% in comparison to the same period last year, making it the second lowest activity level of issuance volume within 10 years since 2013. The total issuance amount across APAC ex-Japan reached USD 352.6 billion over the first 3 quarters of 2023, with 33% and 18% of that volume issued in USD and CNY respectively.
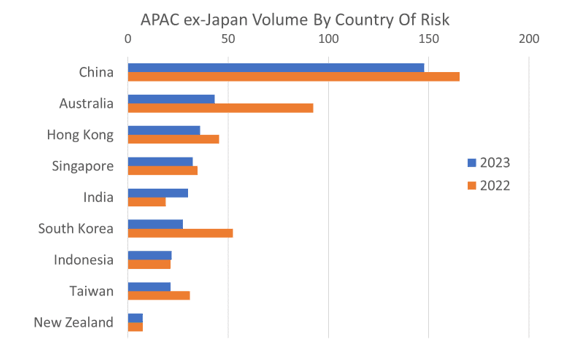
In terms of borrowing volume, China and Australia remained as the two markets with the highest demand throughout 2023 with market shares of 40% and 12% respectively. While South Korea’s borrowing activity dropped from the 3rd in Q2 to 6th in Q3, Hong Kong came up to take its place with a market share of 10%. For the loans volume issued within Q3, refinancing (33%) and general corporate purposes (18%) accounted for roughly half of the loan purposes, both of which were also the leading use of proceeds in H1.
Bank of China, Industrial & Comm Bank of China and Agricultural Bank of China were the top 3 mandated lead arrangers through the first 3 quarters of this year, with market shares of 20.9%, 3.8% and 3.5% respectively. According to the newly released APAC ex-Japan ex-CNY Loans League Table, Bank of China, DBS and HSBC are the leading mandated lead arranging banks, contributing 4.6%, 4.5% and 4.3% to the total market volume.
Greater China
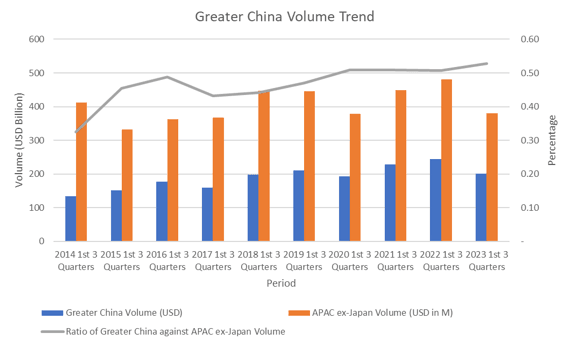
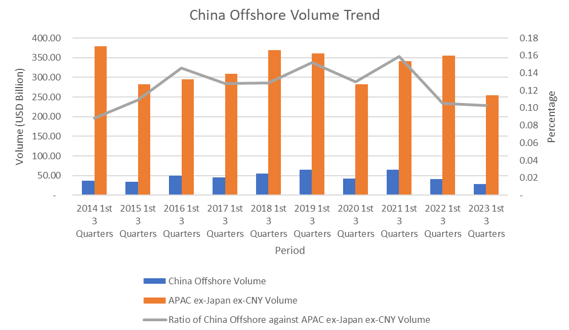
Syndicated lending in Greater China dropped by 17.82% year-on-year, with a total issuance volume of USD 2,006.22 billion so far in 2023, reflecting with the market’s slow performance. The retreat of Taiwanese bank participation in syndicated or club loans to Chinese borrowers is also evident in the drop to 2.21% this year, a record low in the last 10 years. However, the ratio of issuance volume between the Greater China region and the overall APAC ex-Japan region has only slightly increased from 0.51 to 0.53 despite the slow market recovery. According to newly released China Offshore and APAC ex-Japan ex-CNY league tables, the loan volumes in the first 3 quarters of the year saw a 30.23% and 29.40% decrease respectively in comparison to the same time period in 2022, also marking record lows in issuance volume over the past 10 years.
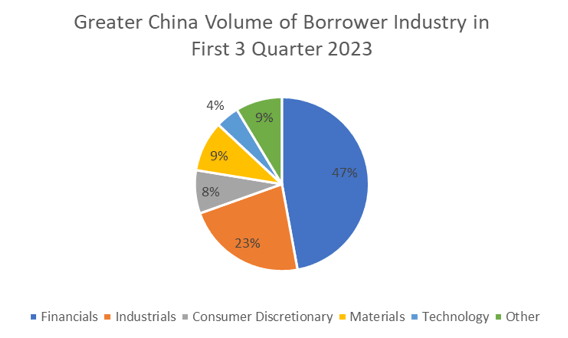
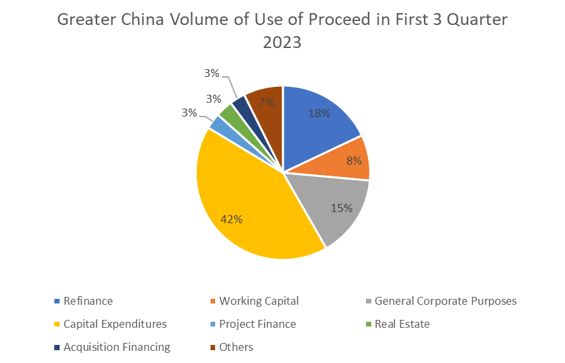
In terms of Greater China borrower industries, Financials and Real Estate remained the most active with 47% in market share, followed by Industrials (23%) and Materials (9%) industries. According to Bloomberg data, the majority of loans issued to real estate companies since Q1 were for refinancing and capital expenditure purposes. With the ongoing debt crisis in the Chinese property sector and restructurings across the larger market, new loan issuance in this region has taken a more conservative turn.
So far this year, the 3 largest deal issuances in the region are with Alibaba Group Holding Ltd for a USD 4 billion syndicated loan, Hai Long 3 Offshore Wind Power Co Ltd for 3.66 billion USD-equivalent, and Sun Hung Kai Properties Financial Services Ltd for 3.51 billion USD-equivalent. Among the mandated lead arranging banks, Bank of China has remained at the top throughout the year, followed by Industrial & Comm Bank of China and Agricultural Bank of China, contributing market shares of 37.30%, 5.97% and 5.69% respectively.
ASEAN
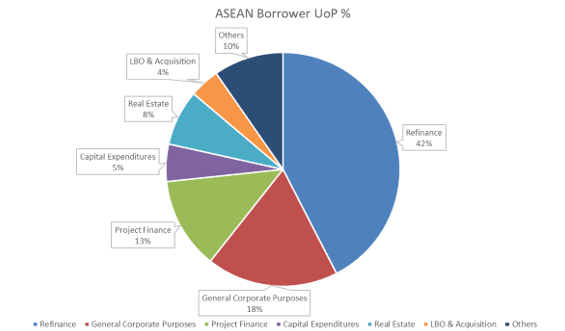
Syndicated borrowing amongst ASEAN borrowers YTD stayed in-line with the activity level seen in 2022 with a modest 2.0% increase YoY, totalling USD 85.2 billion. The region outperformed the rest of APAC ex-Japan, with the sole exception of India. Despite the weak supply of loans in the Greater China region, ASEAN borrowers continue to show an appetite for refinancing (42.4%), general corporate purpose loans (18.2%) and project finance loans (12.7%) this year. The newly released ASEAN Borrower Loans table offers a new borrower’s perspective within the region and bypasses market of syndication discrepancies to reflect the syndicated lending activity in the ASEAN market.
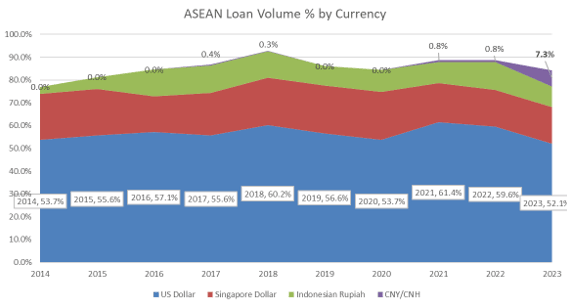
One particular flavor of the year has been the preference for loans denominated in local and regional currencies. US dollar policy rates continue to stay elevated and have pushed the regional borrowers to look at alternative financing currencies. The percentage of syndicated loans denominated in US dollars amongst ASEAN borrowers lost a 7.5% share and experienced a downward trajectory for the second consecutive year, sitting at the lowest level in 10 years. Regional loans in CNY and CNH have always been on the sidelines, until now. The market witnessed a drastic emergence of loans denominated in CNY and CNH this year with 6 deals totaling 6.2 billion USD equivalent and taking up to 7.3% market share. The borrowers on these loans come from diverse backgrounds in transportation, commodities and real estate.
The 3 largest new corporate syndicated loan issuances in the region up till 2023 Q3 were Trafigura Pte Ltd for a USD 2.73 billion equivalent dual currency CNH-USD facility, Vitol Asia Ptd Ltd for a USD 2.60 billion facility, and CIP V Singapore Holding Pte Ltd for a CNY 16 billion facility. Among the mandated lead arranging banks, market shares remain tight between the leading banks as DBS claimed the top spot in the first 3Qs, followed by Oversea-Chinese Banking Corp and United Overseas Bank, making up market shares of 8.49%, 7.31% and 5.33% respectively.
ESG
Sustainable debt financing continues to gain traction in the loan market this quarter. This is partly influenced by the shifts in laws and regulations standards which now emphasize ESG reporting, as well as growing investor interest in ESG-aligned investment opportunities.
One such example within the APAC region would be the 36th ASEAN Exchanges CEO’s Meeting, where the ASEAN stock exchanges developed international-standard sustainability metrics, focusing on governance topics to promote ESG disclosure and sustainable investment. Companies that disclose their ESG goals and progress are better positioned to issue debt, as the transparency allows investors to assess their ability to meet targets.
Despite increased regulatory scrutiny, ESG loans for this quarter increased by 58.03%, compared to the previous quarter, with a total volume of USD 21.275 billion. Out of the total debt issued in Q3, roughly 20.52% account for ESG deals.
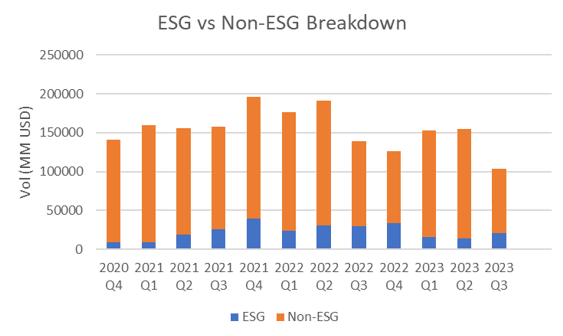
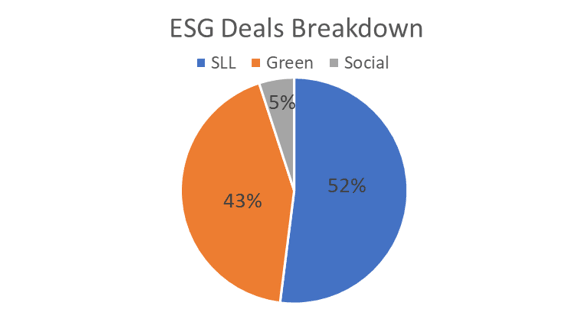
Among the ESG financing instruments, SLL and Green loans remained the most widely issued instrument types, making up 95% of all ESG-related loans. There were no transition finance deals for this quarter.
The largest Green loan for Q3 was the USD 3.66 billion equivalent Hai Long offshore wind project in Taiwan, under a joint venture between Northland and Mitsui & Co. The Hai Long wind project aims to support the Taiwanese government in reaching its renewable energy goal of constructing 15 GW of offshore wind capacity between 2026 and 2035, which would be capable of generating sufficient clean energy for over one million households in Taiwan.
The largest SLL in Q3 was issued in August to Airtrunk, a technology company that provides data center solutions. This AUD 4.6 billion deal is the largest SLL ever secured by a global data center operator, setting sustainability metrics such as carbon usage effectiveness, operating power usage effectiveness, operating water usage effectiveness, gender diversity, and gender pay equity.
As SLLs have gained popularity across the APAC market, the newly created APAC ex-Japan Sustainability Linked Loans table offers regional-focused insights on SLL issuance and complements the regional Green Use of Proceeds table to offer a more holistic view of the ESG loans space in Asia.