APAC loans market had a quiet first quarter in Q1 with volume almost half the size of the previous year. Let’s take a closer look into which specific sectors of the APAC markets are relatively stronger in this dry market.
APAC ex-Japan
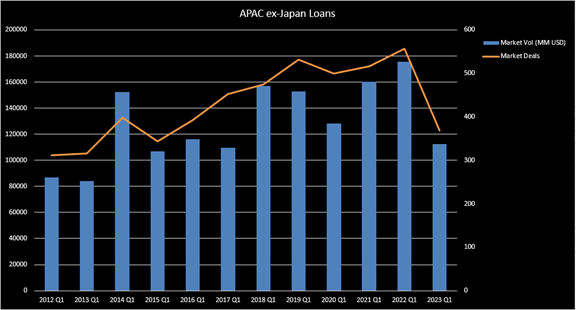
After a year of inflation and rising interest rates, the first quarter of 2023 for syndicated lending in APAC ex-Japan recorded USD 92.62 billion, a significant drop of 46% from USD 172.95 billion in the same period in 2022. Among this volume, Capital Expenditures accounted for 28% followed by General Corporate Purpose and Refinance accounting for 19% and 17% respectively. By industry distribution, the Financials sector borrowing accounted for 45.78% of total issuance, while issuance from Industrial sector and Material sector accounted for 13.96% and 12.77% respectively. In terms of regional breakdown, China borrowers continued to dominate the APAC market by accounting for 41% of APAC Ex-Japan deal volume.
Greater China
Consistent with APAC (Ex-Japan)’s slow performance, syndicated lending in Greater China experienced a sharp drop with a total of USD 48.05 billion in Q1 2023, decreasing by 48.58% year-on-year (yoy). Capital expenditure (CAPEX) financing remained as the highest percentage use of proceeds with 50.1% market share, followed by General Corporate Purpose and Refinancing Loans which made up 18.1% and 16.9% of the market volume respectively. Financial and Real Estate sector accounted for 22.78%, while Industrial sector and Materials sector accounted for 10.86% and 6.89% of total issuance respectively. Of all the issuance in Greater China, 67% of the deals were syndicated in China, 24% in Hong Kong, and 8% in Taiwan.
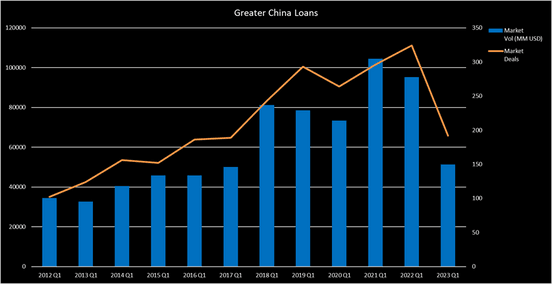
The largest issuance in the region for the quarter was signed by Haitong International Securities Group Ltd for a USD 2.04 billion syndicated loan, arranged by a syndicate of banks led by ABC, BOC, BOCOM, CCB, CMB, HSBC, Huaxia Bank, Industrial Bank, Maybank, Mizuho, SPDB. Sector wise, borrowers in the Financial and Real Estate sector accounted for 22.78%, while Industrial sector and Materials sector accounted for 10.86% and 6.89% of total issuance respectively. Of all the issuance in Greater China, 67% of the deals were syndicated in China, 24% in Hong Kong, and 8% in Taiwan.
Korea
The syndicated loan market in Korea recorded 32 deals in the first quarter of 2023, a significant drop from 103 deals in the same quarter of the previous year. Looking at the past 10 year volume and deal count trend of the 1st quarter of each year, we see an upward trend until 2019 which slowed down in 2020 and 2021 due to the aftermath of Covid. The first quarter of 2022 saw a quick recovery with volumes recording more than double the previous year due to continued low interest rates and the South Korean government’s economic stimulus effort. This spurt, however, was short lived as this year, the loan market was hit with the aftermath of interest rate hikes and as a result the first quarter of 2023 recorded 13.3 trillion KRW accounting to approximately only half the volume of the same period of previous year.
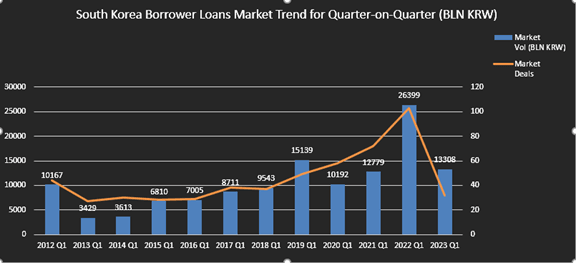
A noticeable deal signed in this quarter is a loan agreement of USD 300 million by Kookmin Bank. The deal, with a 5 year maturity, has a pricing level of .88% points above the 3-month term SOFR rate and includes the condition of receiving an additional rate reduction if the annual ESG target is met. The deal was led by OCBC and includes investors from Singapore, China and Taiwan. With this deal, Kookmin Bank is the first commercial bank to issue Sustainability Linked Loans (SLL) in the Korean market.
ASEAN
As per Bloomberg data, ASEAN syndicated loans market started 2023 with a rise in a total volume of 14.1% as compared to Q1 2022. However, the performance within ASEAN has remained low at around USD 10-15bn since Q1 2020. Specifically, the recorded USD 13.22bn this year was only half the volume of the pre-Covid period in Q1 2019.
The boom in 2018-2019, with a peak of 75 deals in Q1 2019, was primarily due to favorable business conditions from the strong GDP growth, leading to the increased demand for financing. After the 2020 pandemic struck, there has been a decreasing trend with the number of deals. Factors such as the Covid restrictions, continuous rise of interest rates to tackle inflation and disturbances caused by Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, contribute to the increasing uncertainty in investment and rising credit risk which highly impacted the market.
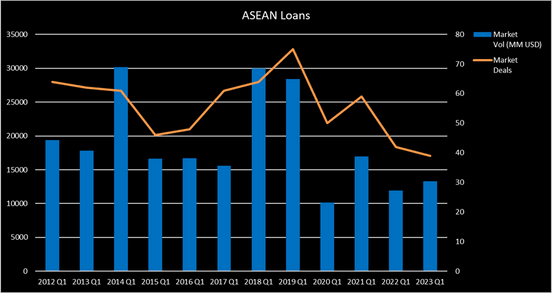
While Financials remains the sector with the highest volume of loans, it is interesting to note that there is a significant increase in the materials sector as compared to the 2022 Q1 by 507.26%. The volatile market conditions caused by the pandemic have led to delays and disruptions in construction projects, where large-scale manufacturing and infrastructure projects are common. This could be a strategic move to ensure a stable supply of raw materials and mitigate the risk of delays and disruptions. This increased demand for syndicated loans within the materials sector can be seen in countries such as Indonesia, which has witnessed a surge in infrastructure projects in recent years, including the country’s capital relocation to East Kalimantan. As the largest economy of SouthEast Asia, Indonesia’s exports increased significantly (climbed by 44.36% year-on-year in March 2022) on the back of rising commodity prices caused by the Russian-Ukraine conflict.

One significant deal in the materials sector of the ASEAN Q1 2023 market was the Lotte Chemical Indonesia PT’s USD 1.77 billion. The borrower, which is a subsidiary of a major chemical Korean company- Lotte Chemical, closed with a maturity of 12 years. This deal is to finance the development of its integrated petrochemical facility, the Lotte Chemical Indonesia New Ethylene Project and attracted a large group of investors globally.