Battery separators’ rapid consolidation heralds one clear leader
This analysis is by Bloomberg Intelligence Senior Industry Analyst Horace Chan. It appeared first on the Bloomberg Terminal.
The lithium-battery separator market’s rapid consolidation leaves Yunnan Energy New Material Co. the dominant producer, with an operating margin now at 30-40% and global market share of 40-50% likely by 2024-25. Japanese and Korean rivals may find it increasingly hard to stay cost-competitive, while their technology leadership gradually narrows.
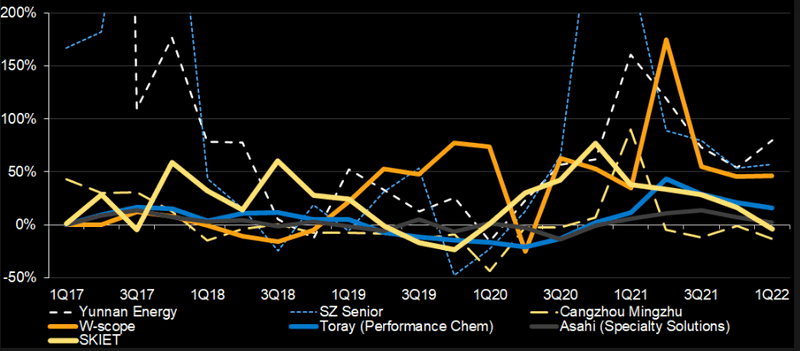
Yunnan Energy emerging as dominant producer
The lithium-battery separator industry could consolidate rapidly, despite speculation in 2020-21 that more new entrants would target such a lucrative space. Yunnan Energy New Material could emerge as the dominant producer with a global market share of 40-50% by 2024-25. This reflects its fast-paced expansion plan, cost control, acquisitions and aggressive financing. Its closest domestic rivals, Shenzhen Senior and Sinoma, are also expanding, leaving smaller players like Cangzhou Mingzhu behind. New entrants such as Hengli may find it difficult to compete on cost and establish a broad client base.
Japanese producers are gradually losing out, mainly because of more conservative growth plans and cost competition, as evident in Toray’s May 2022 decision to book a $170 million impairment loss on related goodwill and fixed assets.
Capacity growth (million square meters)
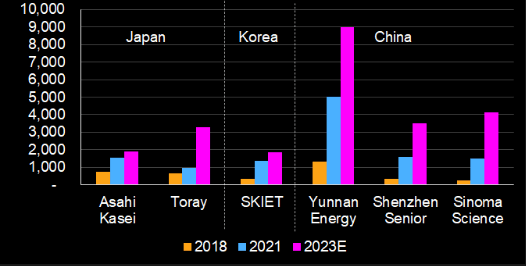
Margin divergence may persist
The profitability of battery-separator producers may continue to diverge into 2023-24. Yunnan Energy may continue to generate 30-40% operating margins due to downward integration of its business to include separator coatings, internal resource recycling, on-line coating methods, solid yield ratios and continued expansion. Newcomers and smaller-scale producers in China risk operating around or even below breakeven level due to competition. Japanese producers may maintain relatively stable percent margins in the high single digits due to long-term contracts with their respective customers. SKIET’s margin may stabilize into 2H22 after it ramped up new facilities.
Operating margins on separators
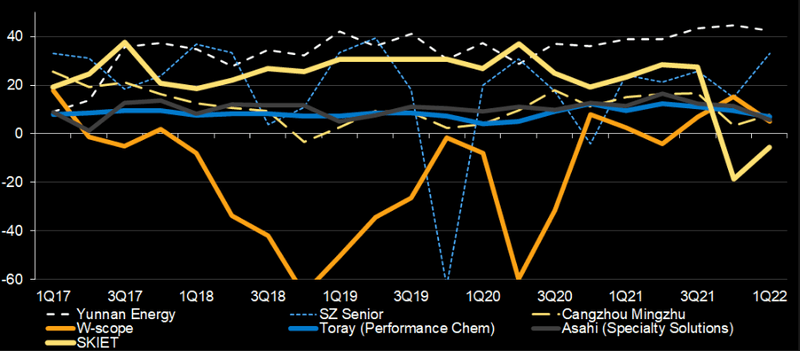
Cost, technology hurdles bar new entrants
Entry hurdles for the battery-separator market have steepened over the past year. It would be tough to be more cost-competitive than the Chinese majors, who adopt aggressive expansion strategies and could squeeze out small producers. Quality control, or yield ratios, pose another entry barrier, as new entrants may find it tough to manufacture consistent products and obtain customer certification.
Japanese and Korean battery-separator producers still have the technology lead, particularly in alternative, non-woven base materials. Toray’s non-porous separator initiative could further enhance battery safety. Yet Chinese majors are also gradually catching up on R&D and now have their proprietary separator-coating facilities.
Separator technology road map / Market growth
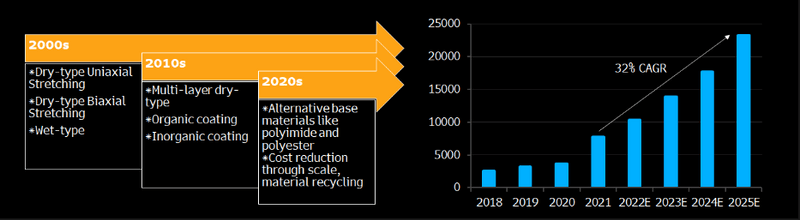
Market rewarding aggressive producers
The separator market could grow an average 32% a year in 2021-25 on our calculations. The most aggressive producers are being rewarded as their volume growth of 50% suggests market-share expansion. The growth path may continue to diverge between the top three companies — Yunnan Energy, Shenzhen Senior and Sinoma — and the rest of the pack. The industry’s worry that solid-state batteries may eventually not require separators may not be a concern at least until 2030, as technologies haven’t reached a commercial scale yet. On the contrary, the first batch of semi-solid state batteries from CATL, Gotion and SES may have stricter requirements for separators’ porosity and physical strength.
Separators’ revenue growth (year on year)