Gen-AI impact poses risk to infrastructure software estimates
Bloomberg Intelligence
This analysis is by Bloomberg Intelligence Senior Industry Analyst Mandeep Singh and Senior Associate Analyst Damian Reimertz. It appeared first on the Bloomberg Terminal.
Gen-AI impact poses risk to infrastructure software estimates
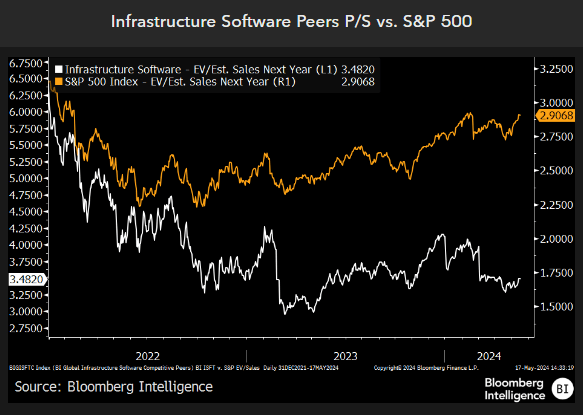
Lower contract duration and pressure on net retention rates (NRR) create risk for pure-play companies across databases, cybersecurity and observability, according to consensus. A 30-50% valuation-multiple compression for a number of the group’s high-growth companies suggests expectations have come down for 2024. Higher compute costs could be a drag on gross margin for smaller vendors.
Gen-AI impact not equal across vendors
Sales consensus cuts remain a risk for high-growth infrastructure-software firms that might not see a boost from generative-AI offerings as enterprise customers shift their IT spending. Overall valuation multiples remain 30-50% below peak valuations in 2021 for a number of pure-play providers. This suggests lower expectations while top-line growth estimates have come down modestly, as was the case with Snowflake.
Exposure to generative AI is expected to boost consumption for cloud vendors in databases, DevOps and observability, driven by the training and fine-tuning of LLMs and the launch of copilot offerings. That could slow investments in traditional data warehousing and analytics initiatives.
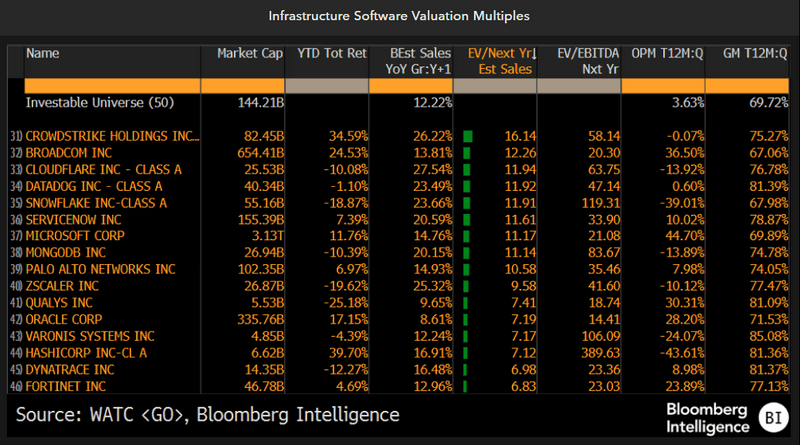
Consumption trends for software peers
Enterprise spending on cloud category leaders in areas such as databases, DevOps and observability may vary depending on their relevance in training and deploying LLMs. Though Microsoft has so far seen the most visible impact from generative-AI offerings to its Azure Cloud growth and the rollout of Office and cybersecurity copilots, we believe there’s room for disappointment at some other high-growth infrastructure-software providers, including Snowflake, Palantir and MongoDB. Snowflake has experienced net retention pressure and is being challenged with an IT-budget shift to generative-AI initiatives from data warehousing, with its own revamped gen-AI product portfolio still in early stages.
CrowdStrike has somewhat bucked the trend compared with peers such as Zscaler, which have seen a significant multiple compression.
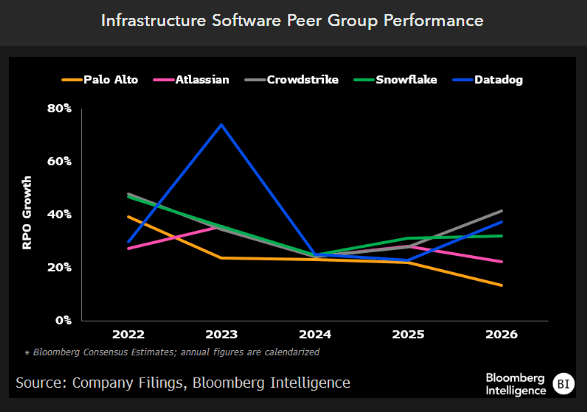
Gen-AI sales delay adds to estimate risk
Though a lapping of cloud optimizations made for easier comparisons, upward sales revisions seem unlikely in 2025 for companies that don’t see incremental revenue from generative AI. Companies including Snowflake and Mongo DB would need to show improved consumption trends to offset headwinds from declining net retention rates and competition from hyperscale providers with integrated LLM offerings. The addition of gen-AI capabilities will likely weigh on the gross margin of most pure-play companies, which could see increased compute costs for gen-AI workloads.
Within cybersecurity, CrowdStrike, with a multiple expansion of around 20% year to date, has benefited from vendor consolidation, which is in stark contrast to a sharp multiple compression for Zscaler.